こちらの製品はDADISICKが独自に開発・製造・販売しているブランド製品です。
安定した高品質の製品を提供し、迅速な納品を保証します。

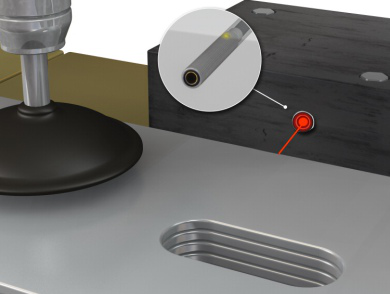




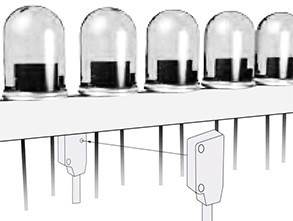




| Photoelectric Sensors GM12 Series | ||
| Series | ||
Size | Cylindrical M12 mm | Cylindrical M12 mm |
Material | Nickel-copper alloy | |
| Reflection method | Diffuse | Through-beam |
| Detection Distance | 20-100 mm; 20-200 mm; 20-300 mm | 2000 mm, 5000 mm |
Output Mode | NPN NO / NC, PNP NO / NC | |
Repeat Accuracy | <5% | |
| Response Time | <5ms | |
Wire Outlet Method | 3pin/4pin with 2M cable | |

| Photoelectric Sensors GM18 Series | |||
| Series | |||
Size | M18 x 73 mm | M18x55 mm,M18x73 mm | Cylindrical M18 mm |
Material | Nickel-copper alloy | ||
| Reflection method | Retro-reflective | Through-beam | Diffuse reflection (adjustable) |
| Detection Distance | 2000 mm, 3000 mm | 5000 mm, 15000 mm | 30-300mm; 50-500mm; 80-1000mm |
Output Mode | NPN NO / NC, PNP NO / NC | ||
Repeat Accuracy | <5% | ||
| Response Time | <5 ms | ||
Wire Outlet Method | 3pin/4pin with 2M cable | ||

Size | 28.4*13*7.5 mm | |
Casing material | SUS316L | |
| Reflection method | Diffuse | Through-beam |
| Detection Distance | 2-50mm | 2000mm |
Light spot size | ф4mm | ф3.5mm (Distance is 500mm), ф7mm (Distance is 1000mm) |
Hysteresis | Less than 20% of the detection distance | |
| Power supply voltage | DC 12~24V | |
Response frequency | 1ms | |

Size | 47*32*21 mm | |
Casing material | Plastic, ABS | |
| Reflection method | Diffuse reflection | |
| Stable detection distance | 60-1000mm | |
Light spot size (distance) | Φ10-40mm | |
Switch output | NPN/PNP | |
| Response time | 2ms | |
Switching frequency | 450Hz | |

Size | 33*13.7*8 mm | |
Shell material | Plastic, ABS | |
| Reflection method | Diffuse reflection | |
| Stable detection distance | 3 - 120 mm | |
Light spot size (distance) | Φ1.5 mm (at 100 mm) | |
Switch output | NPN/PNP | |
| Response time | <0.6 ms | |
Switching frequency | 800 Hz | |

Size | 10.3*19.3*4.7 mm | ||
Shell material | ABS | ||
| Reflection method | Diffuse reflection | Through reflection | |
Detection method | Front detection | Front detection | Side detection |
| Detection distance | 2~30 mm (White paper) | 300 mm, 500 mm | 300 mm, 500 mm |
Power supply voltage | 12~24V DC ±10% | ||
Protection circuit | Reverse connection protection, short circuit protection | ||
| Response time | 1ms or less (action/reset) | ||
Connection method | Wire lead type (2m) | ||

Size | 32*23*12 mm | ||
Casing material | PC | ||
| Reflection method | Diffuse reflection | Specular reflection | Direct reflection |
Detection object | 100*100mm white drawing paper | Objects with a diameter of ≥5mm | Opaque objects with a diameter of ≥12mm |
| Detection distance | 30-150mm (adjustable) | 2M | 10M |
Power supply voltage | DC12-24V | ||
Protection circuit | Surge protection circuit, short circuit protection, reverse polarity protection | ||
| Response time | Action/recovery 1.0ms or less each | ||
Connection method | Wire lead type (standard wire length 2m) | ||

Size | 22*11*8 mm | |
Working voltage | 12-24V DC | |
| Reflection method | Through-beam | |
| Detection distance | 150cm | |
Light source | Infrared LED (940nm) | |
Output | NPN or PNP collector open circuit | |
| Response time | <1ms | |
Entry cable | 2M/3-core cable | |

Size | 21.5*33.3*12 mm | |
Working voltage | 10-30VDC | |
| Reflection method | Diffuse reflection (adjustable) | |
| Detection distance | 30-100mm (adjustable) | |
Light source | Visible LED red light | |
Output | NPN / PNP | |
| Response time | 5ms | |
Standard cable length | 2M | |
| 絵 | Photoelectric Sensors | モデル | 製品の説明 |
|---|